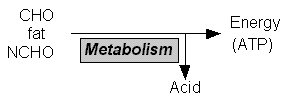
Acid is a waste byproduct of energy production and metabolism, as CO2 (~ 15 mole/day) and as nonvolatile acids (~ 100 mEq/day).
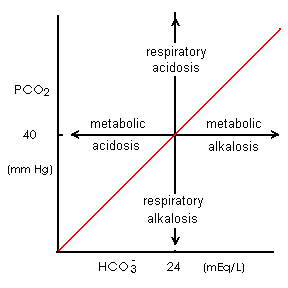
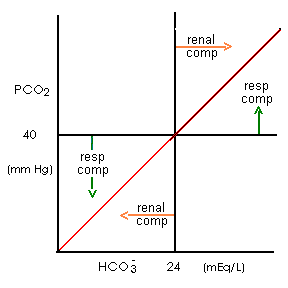
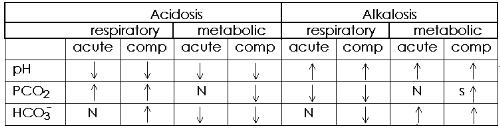
- Respiration eliminates CO2 and normally maintains PCO2 at 40 mm Hg. Respiration rate is controlled by:
- baroreceptors in the carotid arteries responding to PO2
- chemoreceptors in the medulla responding to CSF pH
- The kidneys normally maintain HCO3- concentration at 24 mM. Renal acid elimination rate and rate of HCO3- reabsorption and formation is passively controlled by blood/tubule fluid [H+]. However, the amount of the enzyme, glutaminase, in renal tubule epithelial cells limits the maximum rate of NH3 formation and therefore the maximum rate of renal acid elimination.
- HCO3- serves as a buffer for elimination of H+ as CO2 :
HCO3- + H+ -------> CO2 (with elimination by lungs) - The [HCO3- ] / [CO2] ratio controls blood pH:
- (H+ ) = Ka / [(HCO3- ) / (CO2)]
-log(H+ ) = pH = 6.1 + log[(HCO3- ) / (CO2)]
= 800 nM / [(HCO3- ) / (CO2)]
- (H+ ) = Ka / [(HCO3- ) / (CO2)]
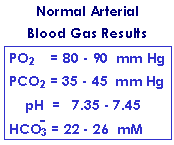
- The Blood Gas CO2 result is expressed in terms of mm Hg.
normal PCO2 = 40 mm Hg
PCO2 results can be transformed to mM concentration units by:- (CO2) = 0.03 x PCO2
normal (CO2) = 1.2 mM - (CO2) = 0.03 x PCO2
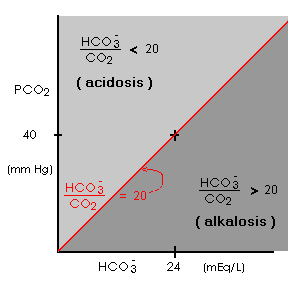
- Since normal (HCO3- ) = 24 mM and normal (CO2) = 1.2 mM:
- normal [(HCO3- ) / (CO2)] = 20
normal (H+) = 800 nM / 20 = 40 nM
normal pH = 6.1 + log(20) = 6.1 + 1.3 = 7.4 - normal [(HCO3- ) / (CO2)] = 20